Australian Asthma Handbook
The National Guidelines for Health Professionals
Definition of asthma and guidance on diagnosing asthma, or confirming the diagnosis, in people 12 years and over.

Adults and Adolescents
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory lung condition, clinically defined by the combination of variable respiratory symptoms…
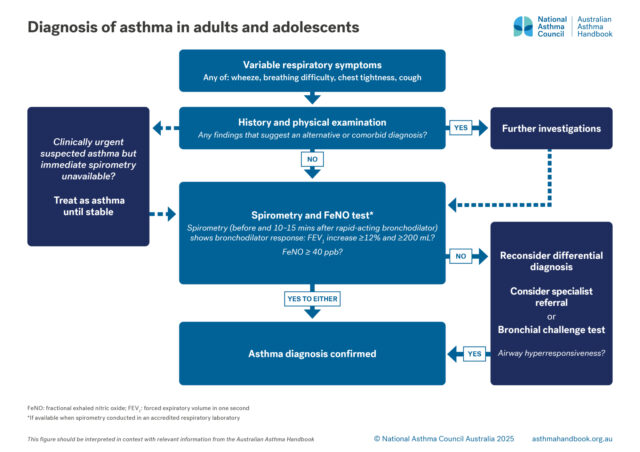
Adults and Adolescents
Investigation of suspected asthma and diagnostic criteria in adolescents and adolescents.

Adults and Adolescents
Why and how to confirm a previous asthma diagnosis, including when the patient is using asthma medicines.